Laissez Faire Economists of the 19th Century Argued That
Laissez-faire is an economic theory that became popular in the 18th century. The meaning of LAISSEZ-FAIRE is a doctrine opposing governmental interference in economic affairs beyond the minimum necessary for the maintenance of peace and property rights.
Laissez Faire Economics Economics Help
Smith argued against mercantilism and was a major proponent of laissez.
. The Court in the middle of the 20th century seemed to have abandoned its old project of imposing an anti-redistributive laissez-faire vision of constitutional political economy. The origin of the term is uncertain but folklore suggests that it is derived from the answer Jean-Baptiste Colbert comptroller general of finance under King Louis XIV of France received when he asked industrialists what the government. Although there is considerable debate as to the defining features of neoliberal thought and practice it is most commonly associated with laissez-faire economics.
Allow to do policy of minimum governmental interference in the economic affairs of individuals and society. The driving principle behind laissez-faire a French term that translates as. How to use laissez-faire in a sentence.
In particular neoliberalism is often characterized in terms of its belief in sustained economic growth as the. From around 1840 to 1860 laissez-faire advocates of the Manchester School and writers in The Economist were confident that their early victories would lead to a period of expanding economic and personal liberty and world peace but would face reversals as government intervention and activity continued to expand from the 1850s. The Austrian School is a heterodox school of economic thought that is based on methodological individualism the concept that social phenomena result exclusively from the motivations and actions of individuals.
The Austrian School originated in late-19th and early-20th-century Vienna with the work of Carl Menger Eugen Böhm von Bawerk Friedrich von Wieser and others. Adam Smith was an 18th-century Scottish economist philosopher and author who is considered the father of modern economics. Later in the 19th century when there began to be a movement away from freer economic arrangements and laissez faire toward a greater measure of collectivism and centralization the view developed as expressed for example by Lord Acton and in the 20th century by Henry Simons and Friedrich Hayek that the relation was more nearly the opposite.
Neoliberalism ideology and policy model that emphasizes the value of free market competition.

Laissez Faire Policies In The Gilded Age Article Khan Academy

Laissez Faire Economics Youtube

Laissez Faire Meaning Economics Examples Policies
/adam-smith-economics_final2-261ec50cfb04406585d7a298858eb4bb.png)
Who Was Adam Smith Why Is He Considered The Father Of Economics

Economics Of The Industrial Revolution The Industrial Revolution Opened A Wide Gap Between The Rich And The Poor While Business Leaders Believed The Ppt Download
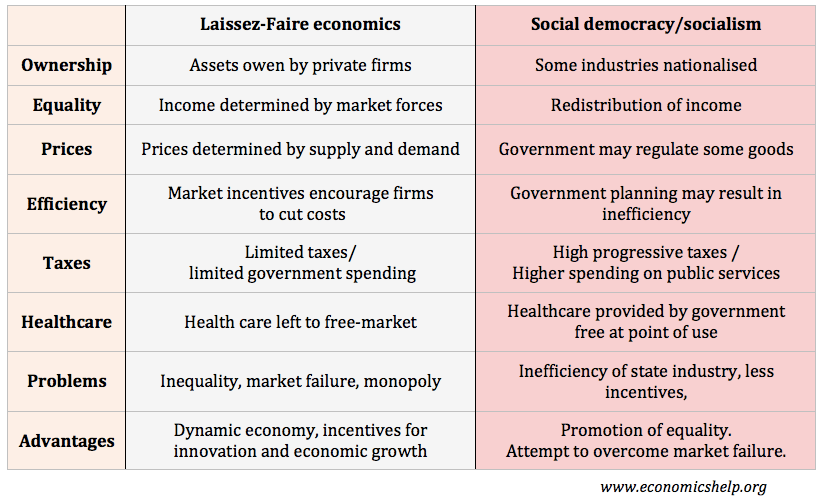
Laissez Faire Economics Economics Help

Agrarian Revolution Event That Sparked The Industrial Revolution New Technologies And Farming Methods Jethro Tull S Seed Drill Enclosure Movement Ppt Download
/laissez-faire-definition-4159781-V2-828107953ee443f1bdeaaaba9b35759b.jpg)
What Is Laissez Faire Economic Theory

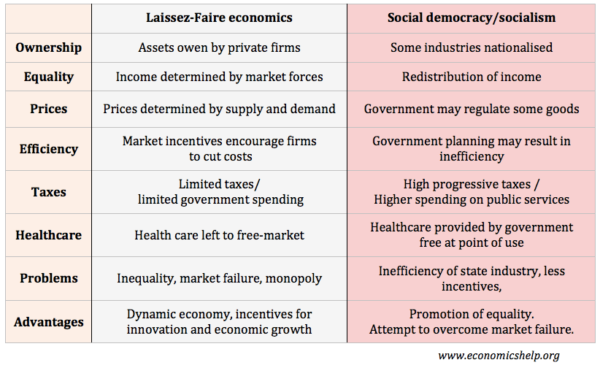
Laissez Faire Economics Economics Help

Laissez Faire Meaning Economics Examples Policies
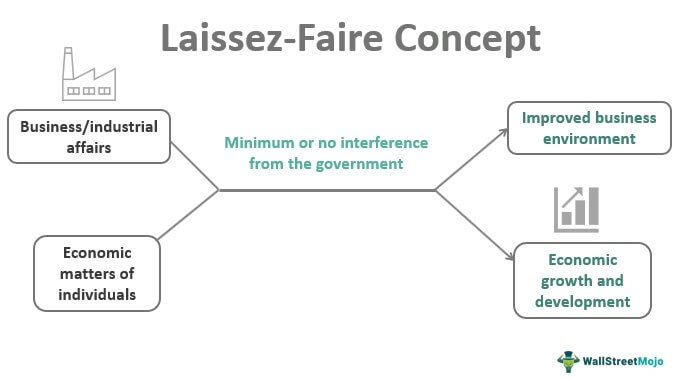
Laissez Faire Meaning Economics Examples Policies

The Progressive Era Timeline Timetoast Timelines

New Ways Of Thinking Economics And Society Ppt Download
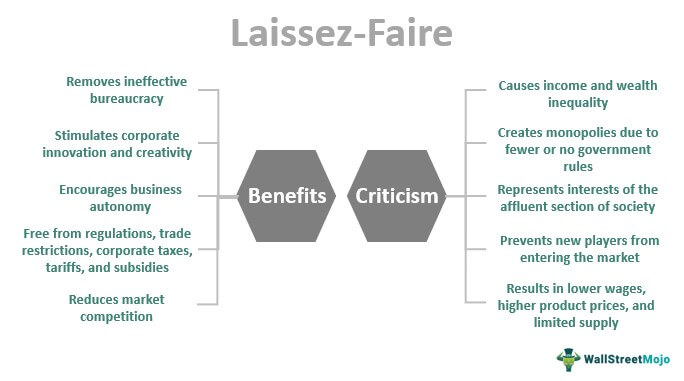
Laissez Faire Meaning Economics Examples Policies

Teri Kanefield On Twitter 2 Notice That The Definition I Cited Explains That Laissez Faire Economics Assumes A Natural Economic Order Laissez Faire Is Justified Based On A Hierarchy Theory Of Government There Is

Laissez Faire Library Of Congress Washington D Neg Co Lc Usz62 76491 Laissez Faire Studocu

Laissez Faire Capitalism History Crunch History Articles Biographies Infographics Resources And More

Laissez Faire Capitalism History Crunch History Articles Biographies Infographics Resources And More
Comments
Post a Comment